Docu review done: Mon 20 Feb 2023 10:59:23 CET
Raid
Table of content
Raid Levels
| RAID Level | RAID 0 | RAID 1 | RAID 4 | RAID 5 | RAID 6 | RAID 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min HDDs | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| functionality | 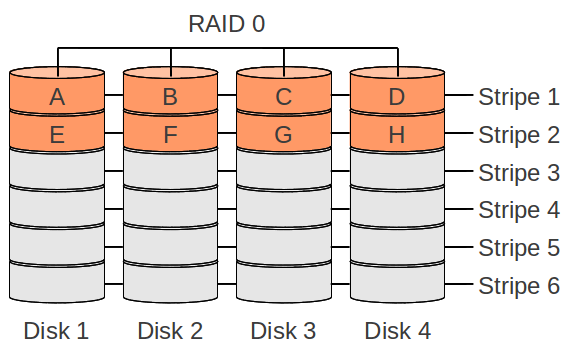 | 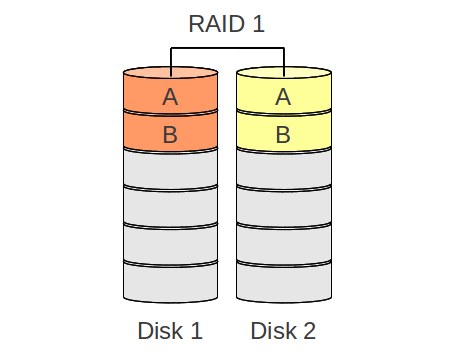 | 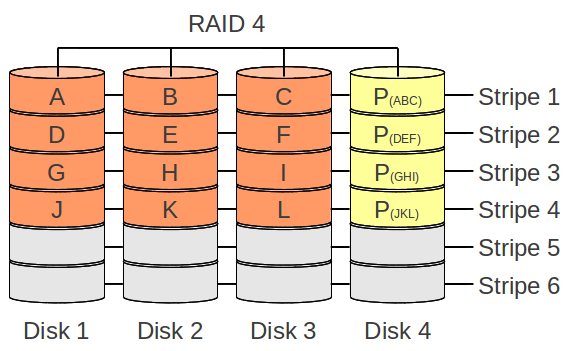 | 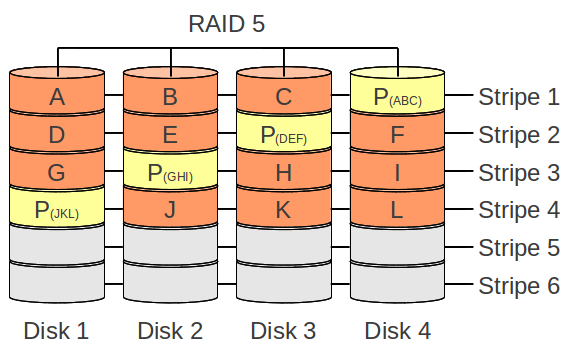 | 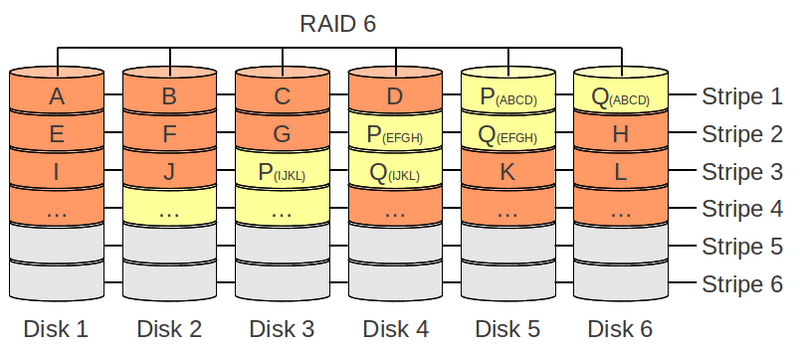 | 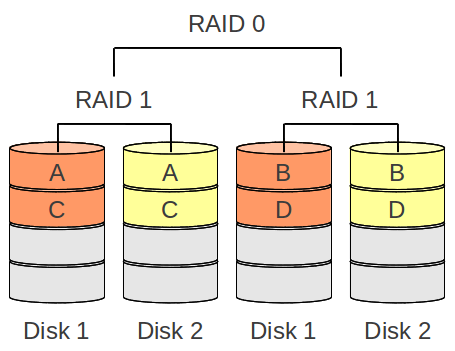 |
| data safety | none | one dead drive | one dead drive | one dead drive | two dead drives | one dead drive per sub-array |
| kapazity | 100% | 50% | 67% - 94% (by 16 drives) | 67% - 94% (by 16 drives) | 50% - 88% (by 16 drives) | 50% |
| rebuild after one drive broke | not possible | copy mirrored drive | rebuild of content with XOR (all drives need to be fully read) | rebuild of content with XOR (all drives need to be fully read) | rebuild of content from initial drive (depending on raid 6 level implementation) | copy mirrored drive |
| rebuild after two drives broke | not possible | not possible | not possible | not possible | same as above | only possible if two drives from differnt raids are effected |
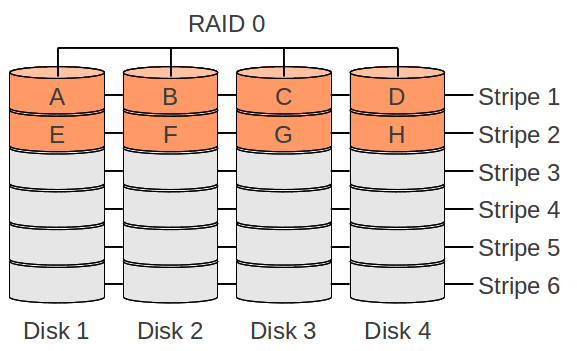
RAID 0
- High performance: for reading and writing multible discs can be used
- No data savety: if one disk breaks the full data is getting lost
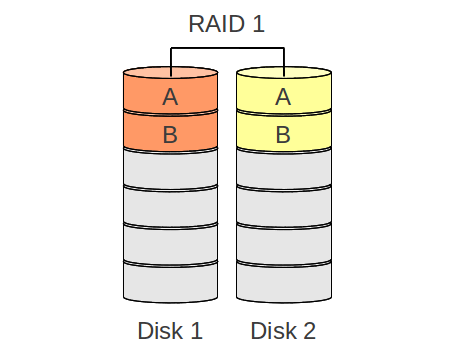
RAID 1
- Performance: for writing operations the spead is nearly the same as if you would write to a single disk and for reading it is possible to read from both which means that the read operation can be improved
- Data savety: the full data is mirrord between the disks/partitions, means one disk/partition can break an no data will be lost
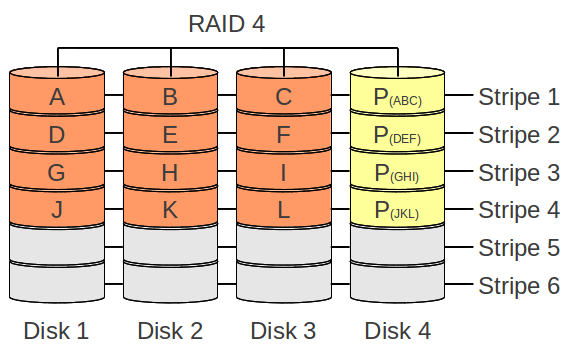
RAID 4
RAID 4 is nearly the same as a RAID 5, besides that the parity data is saved on a dedecated disk/partition and not like in RAID 5 splited over disks/partitions
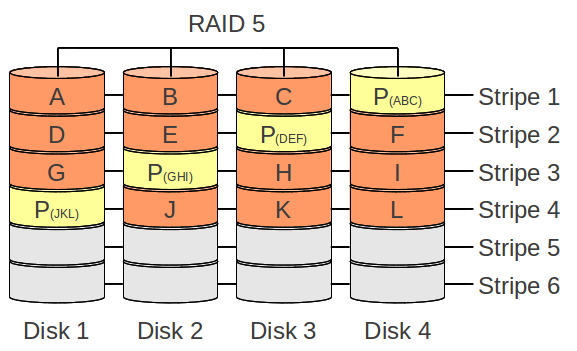
RAID 5
- No data loss on one broken drive/parition
- Parity data: instead of a full data mirror, the RAID 5 calculates the parity data by using a XOR operations
- Destination of parity data: the parity data will be splited around each disk/partition
- High read performance: for huge datastreams the system can get the data from multible disks/partitions
- Write performance: befor the writing operation, a read operations needs to happen for calculating where the new parity data for the stripe needs to be placed.
- Repairing broken disk/parition: If a disk/parition in an RAID 5 fails, the data will be calculated (XOR) and reads all available disks/partitions content for restoring
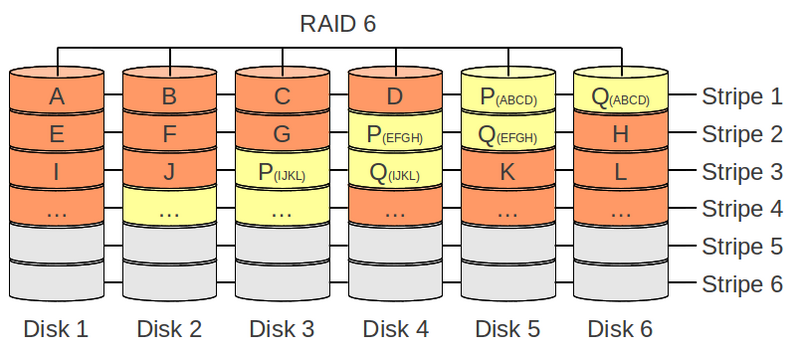
RAID 6
- Corruption of two disks will cause data loss
- Different RAID 6 implementations: there are several different mathematical posibilities for creating and mantaining duplicate parity data (e.g. Galois field or RAID DP)
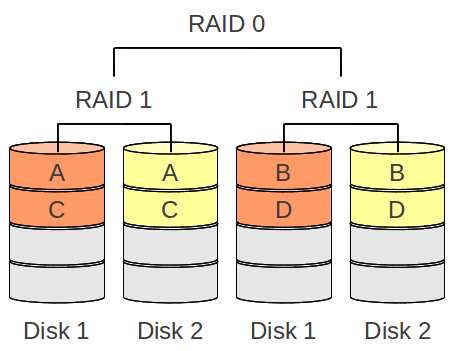
RAID 10
High performance same as RAID 0 combined with data savety from RAID 1.