Docu review done: Thu 29 Jun 2023 12:33:28 CEST
Table of content
Simple commands
Insets one record into the table [table_name]
INSERT INTO [table_name] ([column1],[column2],[column3],..) VALUES ([value1],[value2],[value3],..);
Updates record(s) on table [table_name]
UPDATE [table_name] SET [column1] = [value1], [column2] = [value2], ...;
Joins
A JOIN clause is used to combine rows from two or more tables, based on a related column between them.
(INNER) JOIN: Returns records that have matching values in both tablesLEFT (OUTER) JOIN: Returns all records from the left table, and the matched records from the right tableRIGHT (OUTER) JOIN: Returns all records from the right table, and the matched records from the left tableFULL (OUTER) JOIN: Returns all records when there is a match in either left or right table
Inner Join
The INNER JOIN keyword selects records that have matching values in both tables.
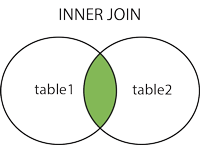
Inner Join Syntax
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
INNER JOIN table2
ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
Inner Join Example two tables
SELECT Orders.OrderID, Customers.CustomerName
FROM Orders
INNER JOIN Customers ON Orders.CustomerID = Customers.CustomerID;
Inner Join Example three tables
SELECT Orders.OrderID, Customers.CustomerName, Shippers.ShipperName
FROM ((Orders
INNER JOIN Customers ON Orders.CustomerID = Customers.CustomerID)
INNER JOIN Shippers ON Orders.ShipperID = Shippers.ShipperID);
Left Join
Left Join Syntax
The LEFT JOIN keyword returns all records from the left table (table1), and the matched records from the right table (table2). The result is NULL from the right side, if there is no match.
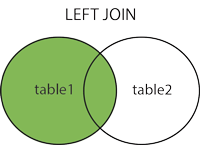
In some databases
LEFT JOINis calledLEFT OUTER JOIN.
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
LEFT JOIN table2
ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
Left Join Example
SELECT Customers.CustomerName, Orders.OrderID
FROM Customers
LEFT JOIN Orders ON Customers.CustomerID = Orders.CustomerID
ORDER BY Customers.CustomerName;
Right Join
Right Join Syntax
The RIGHT JOIN keyword returns all records from the right table (table2), and the matched records from the left table (table1). The result is NULL from the left side, when there is no match.
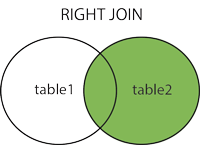
In some databases
RIGHT JOINis calledRIGHT OUTER JOIN.
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
RIGHT JOIN table2
ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
Right Join Example
SELECT Orders.OrderID, Employees.LastName, Employees.FirstName
FROM Orders
RIGHT JOIN Employees ON Orders.EmployeeID = Employees.EmployeeID
ORDER BY Orders.OrderID;
Full Join
Full Join Syntax
The FULL OUTER JOIN keyword returns all records when there is a match in left (table1) or right (table2) table records.
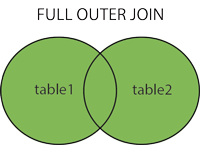
FULL OUTER JOINandFULL JOINare the same.
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
FULL OUTER JOIN table2
ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name
WHERE condition;
SELECT column_n_name = table2.column_name;
Full Join Example
SELECT Customers.CustomerName, Orders.OrderID
FROM Customers
FULL OUTER JOIN Orders ON Customers.CustomerID=Orders.CustomerID
ORDER BY Customers.CustomerName;
Self Join
Self Join Syntax
A self JOIN is a regular join, but the table is joined with itself.
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1 T1, table1 T2
WHERE condition;
Self Join Example
SELECT A.CustomerName AS CustomerName1, B.CustomerName AS CustomerName2, A.City
FROM Customers A, Customers B
WHERE A.CustomerID <> B.CustomerID
AND A.City = B.City
ORDER BY A.City;